An SEO audit uncovers opportunities to improve a website’s search performance. It entails identifying and correcting technical, on-page, content, and link-related issues.
Because there is no universal approach, everyone’s SEO audit process is unique. However, there are a few fundamental issues that all website owners should be aware of.

Performing an SEO audit involves looking for problems or errors that can prevent your website from ranking on Google and other search engines. Several elements make up an SEO audit, including:
- Making certain that Google correctly crawls, indexes, and displays your website
- Looking for faults with your website’s on-page SEO
- Looking for any potential issues with your off-page SEO on other websites that are connected to or link to your site
- Proving the high level of consumer satisfaction on your website
- Making your content keyword-friendly
- Searching your website for redundant or inadequate content
- Creating and keeping up-to-date reporting to track the success of your website
Why is SEO Audits necessary?
With the use of SEO audits, your website and company can avoid:
- Losing organic traffic as a result of lousy site health
- Not taking advantage of sales possibilities or losing ground to rival brands
- Being indexed on search engines
- Being penalized by Google for harmful backlinks
The tools required for an SEO Audit
- Semrush Site Audit Tool – This tool provides a thorough, top-down analysis of the performance of your website. Next, we will delve deeper into the Site Audit tool.
- Google Analytics – Google Analytics provides metrics and data on how well your website performs in their search engine.
- Google Search Console – Using Google Search Console, you can verify if your website is correctly indexed and how it is showing up in search engine results pages.
- Google PageSpeed Insights – PageSpeed Insights rates how quickly and efficiently your website loads on desktop and mobile devices.
- Google Schema Markup Testing Tool – You may test and confirm that your schema is error-free with this tool.
18-Step SEO Audit & Checklist
Let’s start the SEO audit with the things you must always look at. Potential problems, such as serious issues, could be the root of a problem or prevent your website from being effectively crawled and indexed.
Top 21 Best Web Design Agencies in 2022

1. Compare your rankings and learn about your competitors – SEO Audit
Before diving extensively into a technical SEO audit or on-page assessment, it is essential to understand the competitors.
Whether creating a new site for the first time or auditing as part of your ongoing plan, the more you know what other businesses in the same market are doing, the higher your chances of success will be. You must benchmark your website’s rankings and profile your success relative to the competitors.
2. Examine Google’s Index for duplicate versions of your site – SEO Audit
Although it may be the most straightforward test you can perform on your website, it is crucial to ensure that Google only indexes one version of it.
These are different versions of the webpage as seen by a search engine. Only one website version should be indexed, and you must look for duplicate content. If you notice that there are different site versions, there might be an issue.
The other option is to type each URL variation into your browser manually. Whichever you choose, you should anticipate being sent to a single version. If not, use a 301 redirect to point to a single performance.
3. Examine your website’s indexed URLs – SEO Audit
Although you can do this check concurrently with the step above, it deserves its section. Look at how many URLs are indexed after you run a Google “site: search.”
You might need to resolve a problem with duplicate or sparse content pages. It’s helpful to know that you may use the Google Search Console Removal tool to de-index or ban specific pages from appearing in the search results. Please note that these must be URLs you control and have submitted to Google Search Console.
4. Examine for manual actions – SEO Audit
This is a manual action when a human reviewer at Google determines that your site does not adhere to their webmaster rules. Your site won’t appear in Google’s search results in whole or in part as a result.
A manual action is not likely to occur unless you’ve done something seriously wrong. However, it’s still conceivably the best thing to check first because if you have one, you’re already out of luck.
Visit the Manual action report in Google Search Console to look for any manual actions.
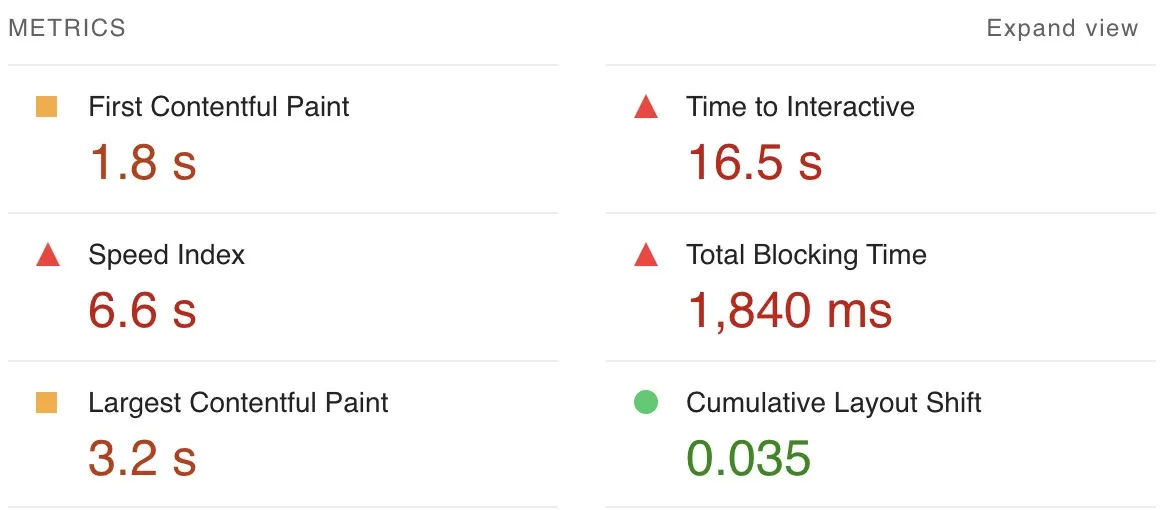
5. Examine the speed of your website – SEO Audit
Page speed has been a minor ranking element on desktops since 2010 and mobile since 2018. A page should load quickly, but there is no standard, and there are a bewildering array of metrics you might use as a substitute. Google, for instance, provides a variety of indicators in its PageSpeed Insights tool:
6. Confirm that your website employs HTTPS.
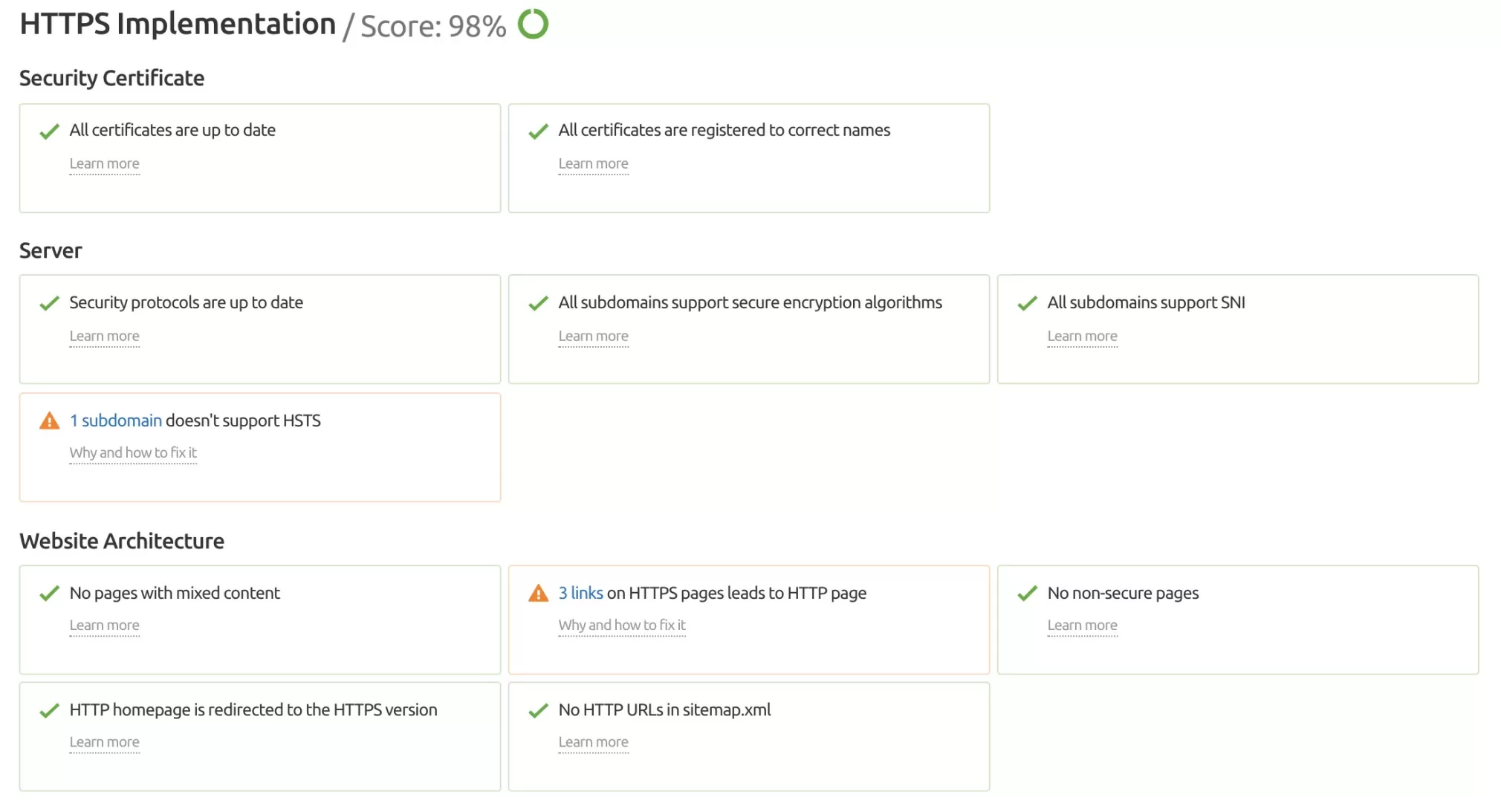
If your website isn’t currently configured for HTTPS, upgrading would be a good idea. That “S” is now referred to as “Transport Layer Security,” having previously been known as “Socket Security Layer.”
To put it simply, the HTTP protocol is just an encrypted form of that “S”. Anyone who visits your website increases the level of cyber security.
Go to Site Audit’s HTTPS report.
SEO Agency | Top 30 SEO Companies Ranked in 2022
7. Examine for mobile-friendly issues
Mobile-friendliness has started to factor into rankings as of 2015. It’s true that most websites are responsive or use distinct mobile-optimized versions, but this does not rule out the possibility of issues.
The Page Experience will be modified to include mobile-friendliness beginning in 2021, arguably the most significant change.
A useful Google tool called the Mobile-Friendly Test can be used to evaluate how effectively mobile versions of websites function.
8. Analyze and resolve any remaining indexation issues
Stay in Google Search Console and navigate the Index tab’s Coverage page. You can see pages that are valid or have warnings, coverage errors, and excluded pages.
Common mistakes include:
- Pages with the noindex attribute that are included in a sitemap
- Pages barred from crawling in your robots.txt file but included in a sitemap
- 404 pages submitted in a sitemap
You must clean up if you find errors and know what caused them.
9. Recognize your site’s page experience
In short, user experience is being used as a ranking factor.
Google responded as follows:
“Today, we’re building on this work and providing an early look at an upcoming Search ranking change that incorporates these page experience metrics. We will introduce a new signal that combines Core Web Vitals with our existing signals for page experience to provide a holistic picture of the quality of a user’s experience on a web page.”
10. Examine your On-Page SEO
On-page SEO includes things like:
- Title tags, meta descriptions, and header tags should all be optimized
- Including helpful image alt tags
- Developing optimized content
- Putting together an internal linking structure
Auditing on-page SEO elements is critical because these optimization opportunities are under your control.
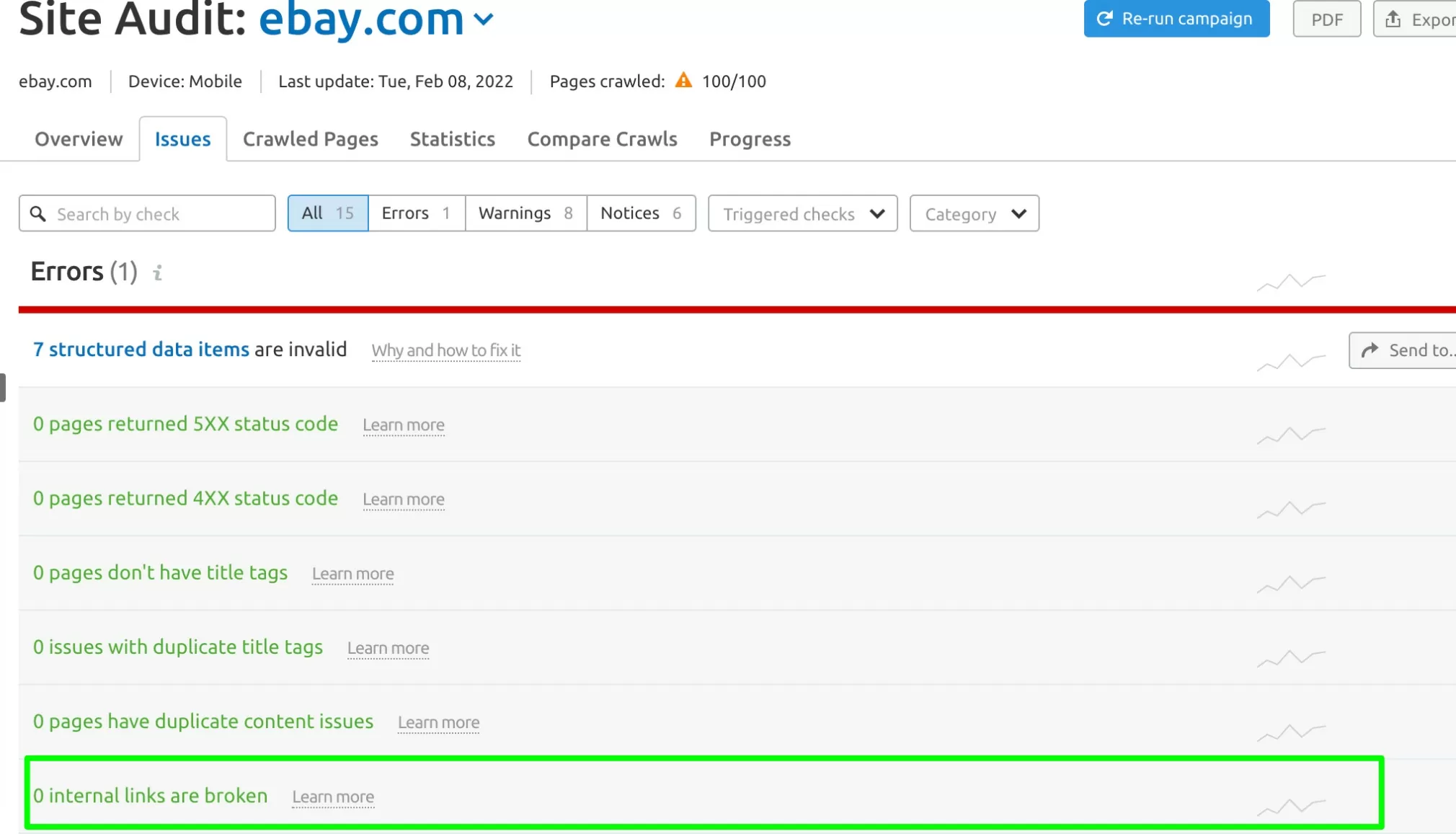
11. Fix Internal Links that are broken
Broken internal links create a negative user experience. Users who click a link on your site expect to be taken to that page rather than being served a 404 error. However, it sends negative quality signals to search engines.
Broken internal links are highlighted in the Site Audit report’s issues tab.
Top 10 Web Development Companies In The World With Review
12. Organize your sitemap
The XML sitemap for your site shows Google the primary pages on your site to index.
Issues with incorrect URLs in your sitemap will be presented as errors in your Site Audit report.
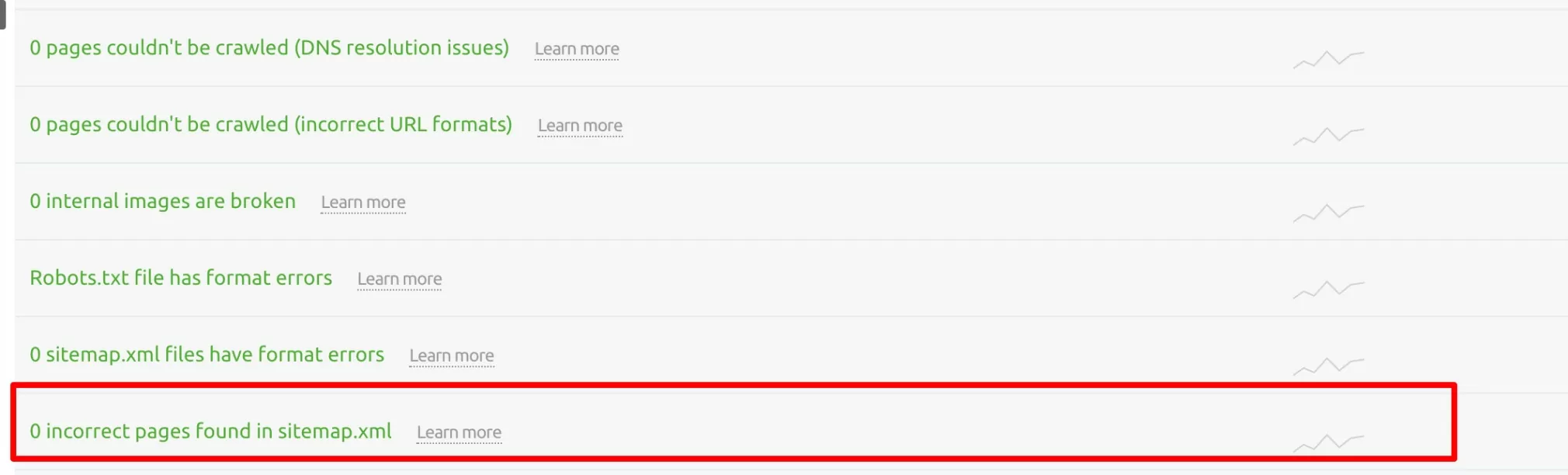
These errors occur if your sitemap file contains URLs that lead to pages with the same content, redirect to another page, or return non-200 status codes.
As a quick fix, prioritize removing any incorrect pages from your sitemap.
13. Examine your redirects
Discovering redirection issues is uncommon, but locating and resolving these is usually a simple process.
The Site Audit report identifies several redirect issues.
- Chains and loops should be redirected
- Temporary Redirects
- Examining the Content of Your Website
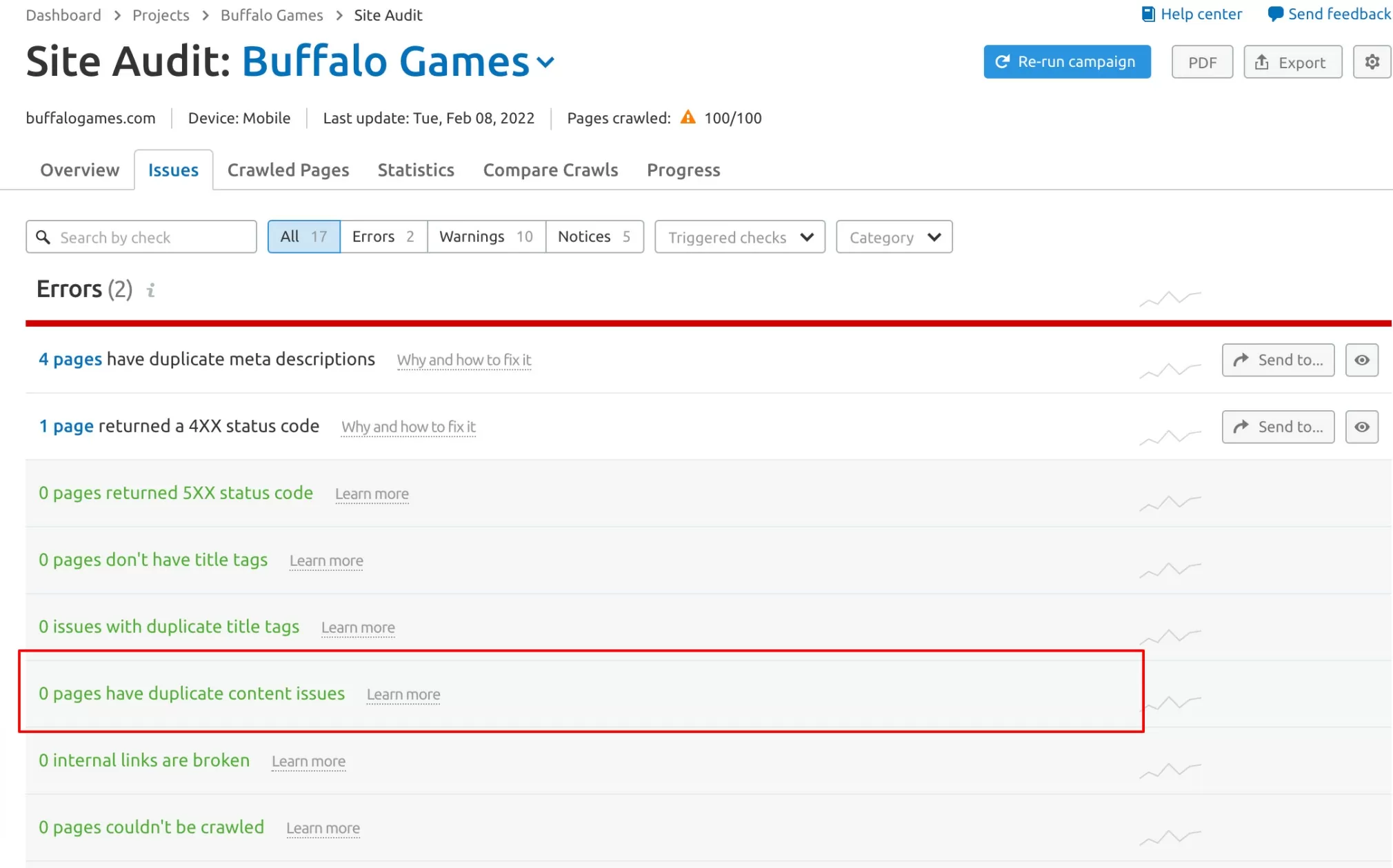
14. Locate and correct duplicate content issues
Duplicate content on your site can cause problems, preventing you from ranking as high as possible. It has the potential to confuse search engines.
Duplicate content issues can be found on the Site Audit report’s issues tab.
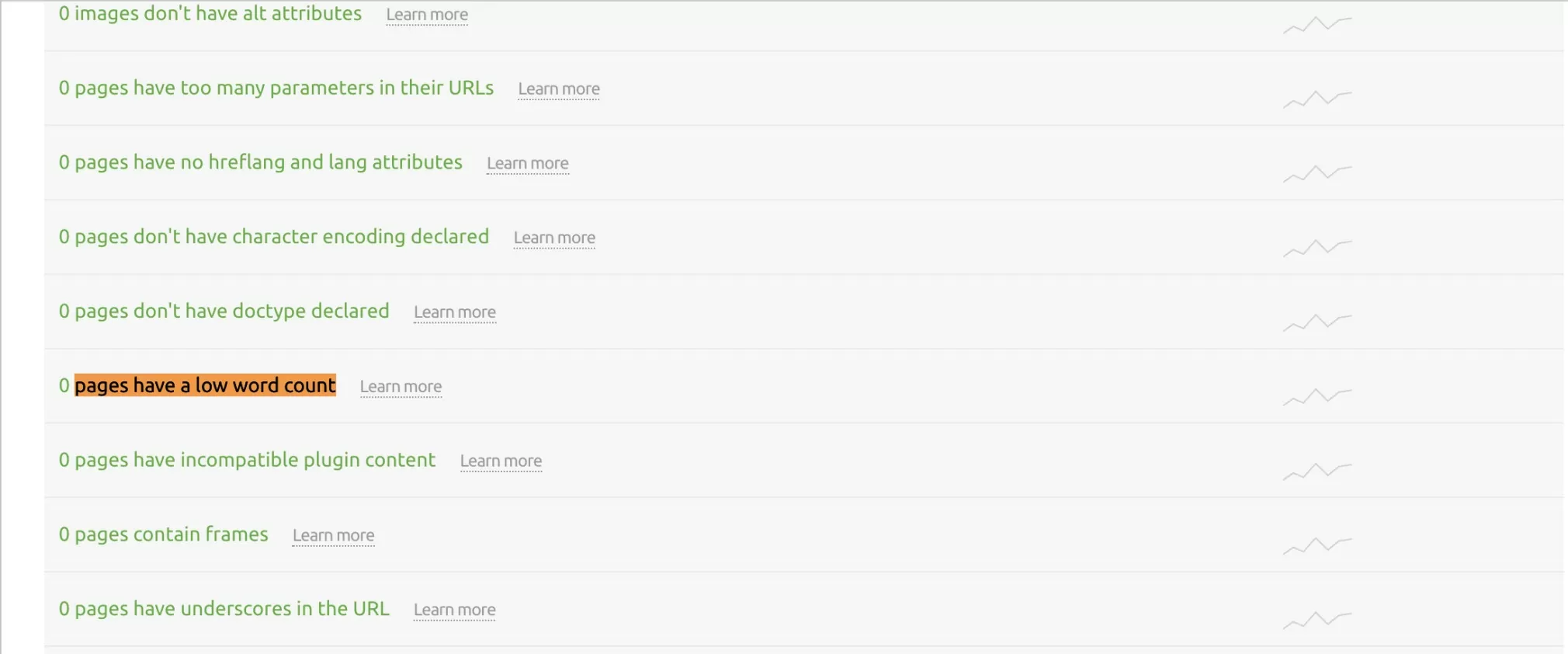
15. Determine thin content pages
While it is not a direct ranking factor, it is important to ensure that your content provides sufficient context and information for the topic you are writing about.
Pages with thin content provide little or no value to users or search engines. This content is unlikely to convert users and may even turn them off of your website.
These issues will be flagged in your Site Audit’s errors tab; they are reported as pages with a low word count.
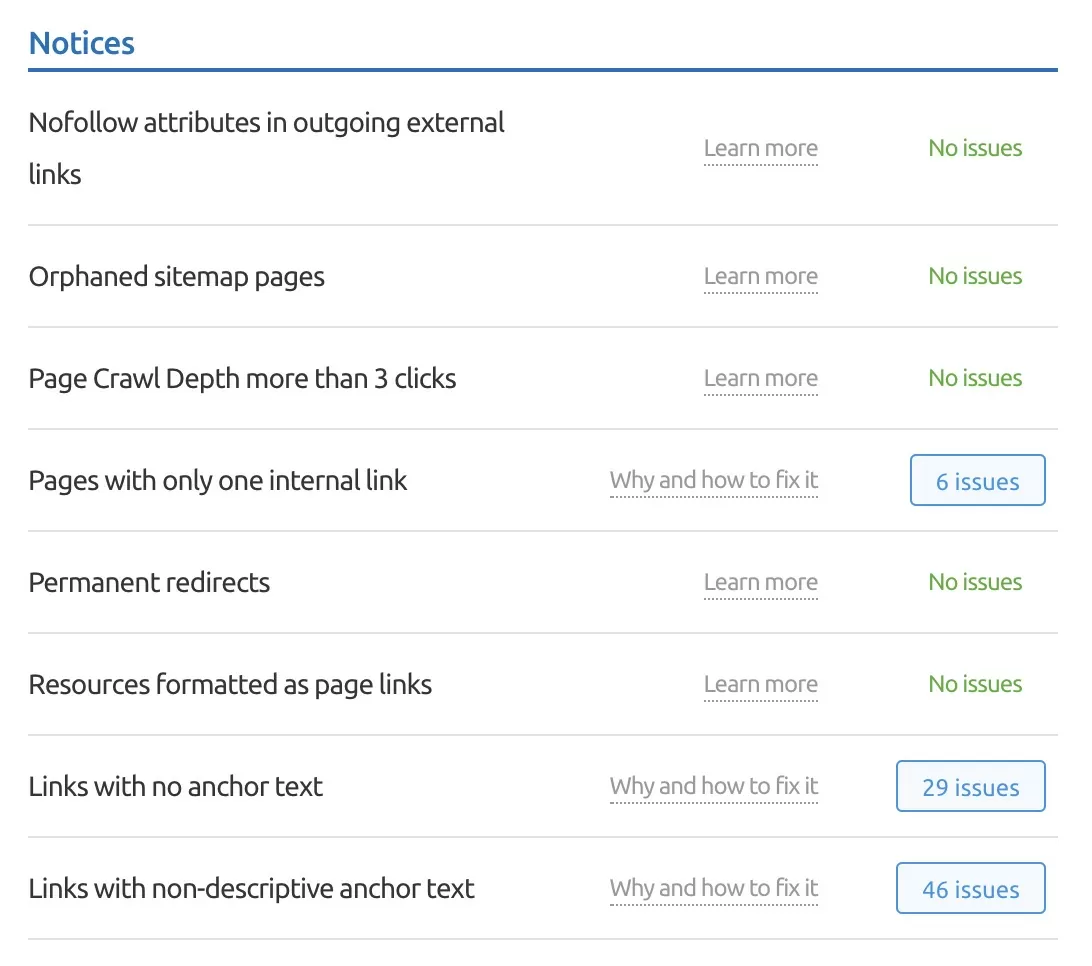
16. Troubleshoot orphan pages
Orphan pages are those that exist on your site but aren’t linked to from anywhere else.
In essence, if a page is not linked to, it is not receiving topical authority passed through internal linking and may be considered a gateway page in rare cases.
Pages that exist in your XML sitemap but are not linked to any other page will be found.
Go to the Internal Linking Report to locate any orphaned sitemap pages or pages with only one internal link.
The simplest solution is to either add key pages to your site’s navigation or include at least one internal link from relevant content.
17. Analyze searcher intent by comparing your content to top-ranking pages
In recent years, one of the most important considerations for SEOs has been searcher intent.
Spend time analyzing the top-ranking pages for the search terms you want to target. Suppose you notice a significant difference between your content and the pages that rank first on Google. In that case, you should consider conducting a content audit to rework your page with searcher intent.
18. Conduct a Backlink Audit
Links continue to be an important ranking factor. Aside from planning a strategy to build more links than your competitors, you can also run a Backlink Audit to check for potentially toxic links.
Not all links will help you rank higher. If Google believes a link is being used to manipulate your search rankings, it violates their Webmaster Guidelines.
It is critical to check for toxic links as part of any SEO audit, especially if you are working on a new site.
Following an SEO Audit, What comes next?

So you’ve completed your SEO audit and discovered numerous areas for improvement. Following the completion of your audit, the following items should be checked off your checklist:
- Monitor your keyword rankings and positions.
- To remove any duplicate content indexed in Google, use the Removal tool in the Google Search Console.
- Remove any clunky programming slowing down your page performance or making Google’s rendering of your site difficult.
- Repair any broken links, convert 302 redirects to 301 redirects as needed, and clean up your sitemap.
- Begin categorizing your backlinks into three major groups and contact publishers/export your disavow list.
- Allow the SEO Writing Assistant to assist you in creating the most unique and original content on the internet.
- Include at least one relevant internal link on any orphan pages you find.
- Begin by running reports through our Reports feature to review and confirm that your hard SEO audit work is paying off. This is especially important for government agencies. You can create customized reports for clients on any aspect of SEO, from technology to content to site audits.
Conducting an SEO audit can assist you in developing a solid strategy at the start of a new project or site launch, which is an essential part of long-term success.
You can fix problems that prevent your site from reaching its full potential by identifying them as soon as possible using the information compiled by EverRanks above.







